end tidal co2 meaning
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation. MONITORING of end-tidal carbon dioxide is one of the most important means of determining the physiologic well-being of anesthetized patients.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
. Savastano S et al. Mean ETCO2 20 mmHg during pediatric in-hospital CPR was not associated with survival to hospital discharge and ETCO2 was not different in survivors versus non-survivors. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg.
When the measurement is taken at the end of a breath exhaling it is called end tidal CO 2 ETCO 2. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled.
The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. This is a major respiratory symptom.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. Normal end-tidal capnography is.
This monitoring is often employed in PACU and procedurepost procedure areas. Can the value of end tidal CO2 prognosticate ROSC in patients coding into emergency department with an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Sometimes however etCO 2 monitoring is used as a feedback or biofeedback mechanism.
Carbon dioxide CO 2 is a product of metabolism transported via perfusion and expelled through ventilation. Mengert The New England Journal of Medicine. But ETCO2 can also provide valuable information on the adequacy of cardiac perfusion.
Low EtCO 2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. Exhaled carbon dioxide both in terms of its quantity and pattern provides detailed information on the cardiopulmonary system.
In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. Eisenberg and Terry J. Like pulse oximetry before it alerting us to changes in oxygenation end-tidal CO2 monitoring or ETCO2 is rapidly becoming an additional vital sign.
End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring is a noninvasive method of measuring exhaled carbon dioxide. Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood.
Of or relating to the last portion of expired tidal air End-tidal carbon dioxide monitors are already being used and are recommended to indicate the adequacy of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and the likelihood of a successful resuscitation. End Tidal CO 2 6 Can also be measured and monitored in spontaneously breathing patients via nasal cannula or mask see pictures below Same connectors and monitor would be used as seen on previous slides. When the spontaneous breathing of the patients started their respirations were supported as the end-tidal carbon dioxide ETC Osub2 value would be 35-40 mmHg.
End tidal carbon dioxide concentration. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal capnography is a measurement of carbon dioxide partial pressure measured in millimeters of mercury which is useful in assessing a patients ventilation.
We routinely use ETCO2 to provide information on ventilation. In critical care End Tidal CO 2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism which gets transported in the blood to the lungs for elimination.
Citation needed The capnogram is a direct monitor of the inhaled and exhaled concentration or partial pressure of CO 2 and an indirect monitor of the CO 2 partial pressure in the arterial blood. Medical Definition of end-tidal. However EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube ETT P osition CPR Q uality R eturn of spontaneous circulation ROSC S trategies for treatment and T ermination.
End-tidal carbon dioxide during pediatric in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood. End-tidal CO 2 monitoring has also been useful for breathing retraining as it provides additional information about the progress of a persons breathing normalization.
The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at rest is 40 mm. This technique is often used in patients who are not intubated although it is commonly used in intubated patients receiving mechanical ventilation. End-tidal carbon dioxide and defibrillation success in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
In the ED we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation. End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 waveform monitoring allows you to measure all three. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45.
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

E Learning Basics Of Capnography Youtube

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
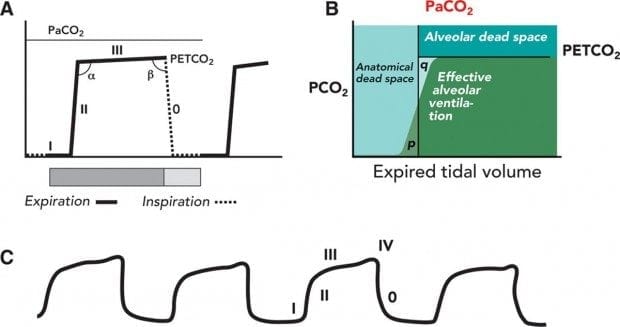
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Normal And Abnormal Capnography Waveforms Infographic Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

